Citation count
A citation count measures the number of times a publication (usually a journal article or conference paper) has been cited in later publications. There are a number of online tools and databases that will help you locate citation counts. None of these are completely comprehensive so checking your citation count in more than one is a good idea.
There are a number of issues to consider with regard to citation counts. A high count isn’t always an indicator of quality. Some publications are cited because they are examples of poor research, are controversial or are rejoinders to more prominent works. Citations may also result from an author citing their own work.
The three main databases that can be used to find citation counts and measures are:
- Scopus
- Web of Science
- Google Scholar
These databases are available through the RMIT University Library website. They are all linked on the Research Metrics subject guide, on the Citation Impact page.
You might like to open this page now in a new tab in your browser. You will be using these databases in the activities that follow.
Come back to this page, to continue working through this module.
 Activity
Activity
Go to Google Scholar and search for one of your own papers or perhaps a colleague’s or supervisor’s.
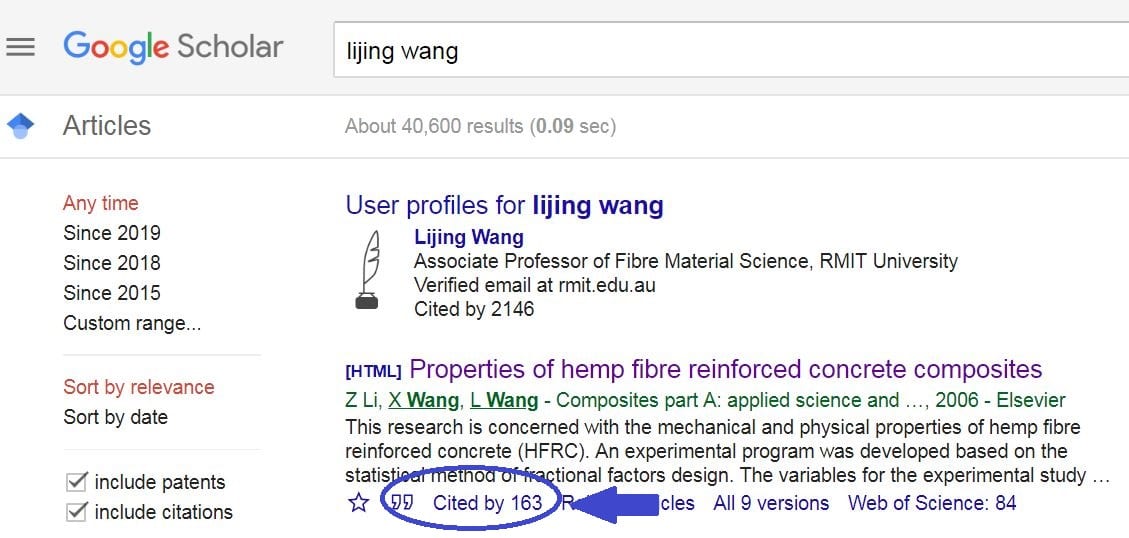
Note the citation count. You can see an example of what you are looking for below.
Image: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google LLC, used with permission.
Now go to Web of Science and search for the same paper. Does Web of Science have the same or similar citation count?